intro-to-galaxy-ngs-sarscov2
Read Alignment
Read Alignment is the process of comparing short reads with a reference genome to find the best-matching position. The Burrows-Wheeler Aligner (BWA) is a fast and accurate tool for both short and long read alignment, and JBrowse is a tool that enables viewing of the alignment results within the Galaxy interface.
Step 1: BWA alignmnent
The naive method of comparing each read in our dataset to each position in the reference sequence is too slow. Therefore, BWA builds an index of the reference sequence, which can be thought of as a lookup table for substrings present in our reference sequence. A short read can be compared to this lookup table in order to find potential matches. For more information on the Burrows-Wheeler Transform, see Stanford CS262 Lecture*
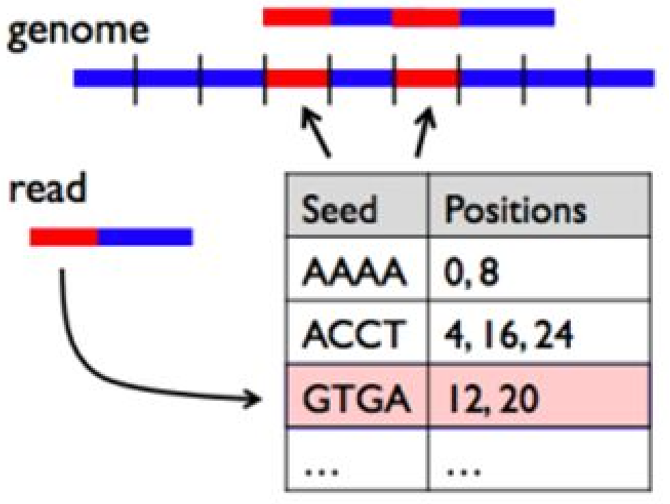
BWA builds an index of the reference sequence.
To run BWA:
- In the Tools panel search bar, type BWA and under the Mapping section, select Map with BWA
- Under Will you select a reference genome from your history or use a built-in index? select Use a genome from history and build index.
- Under Use the following dataset as the reference sequence select 1: genome (as fasta)
- Under Select input type select Paired fastq collection
- Under Select a paired collection select 4: Pair-end data (fasterq-dump)
- Check that your tool is configured as below
- Click Execute
- Once the job is completed, you can preview the resulting SAM file by clicking the
 icon in the completed Map with BWA dataset.
icon in the completed Map with BWA dataset.
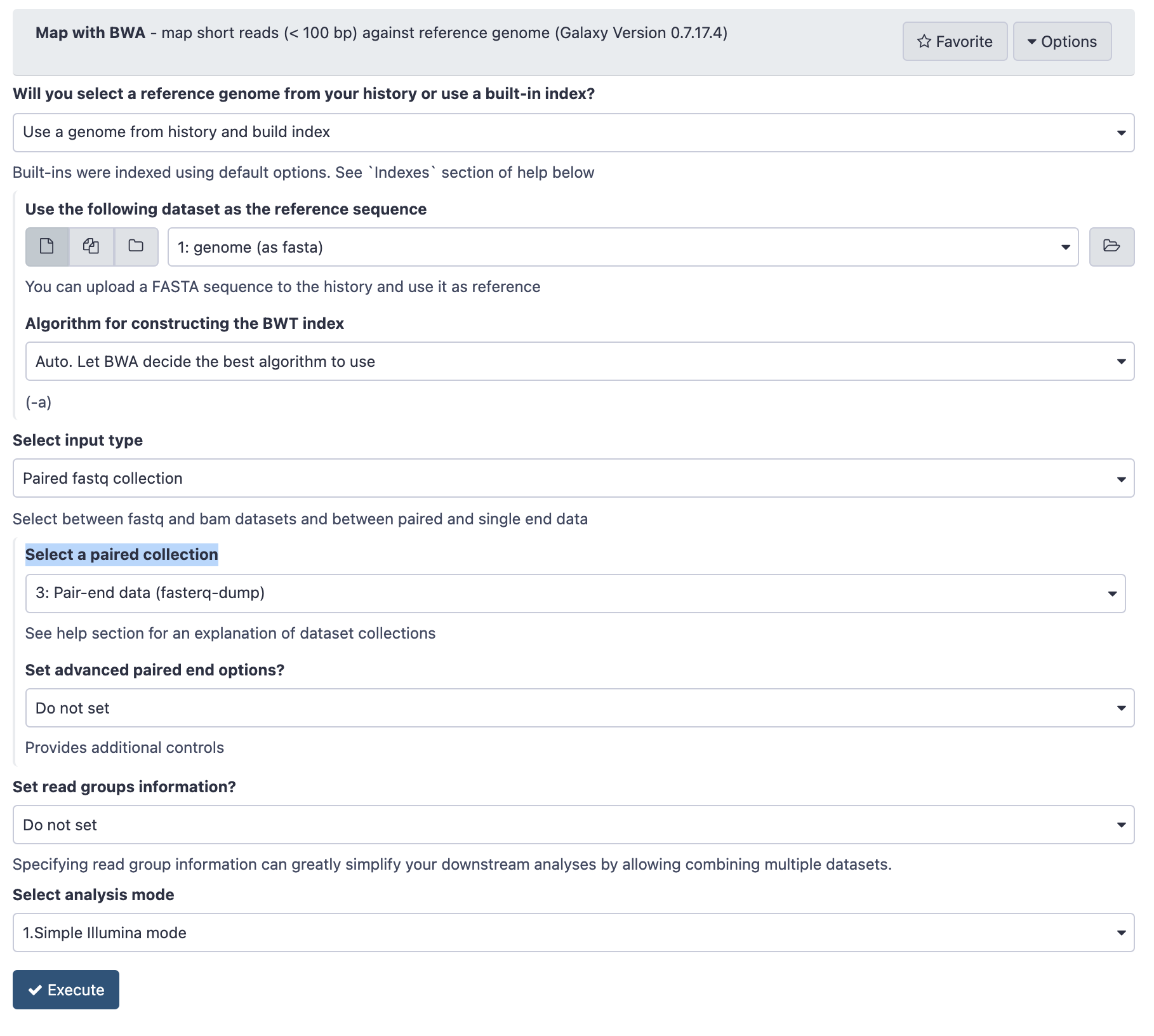
Configuration of BWA
SAM format
BWA produces a BAM file, which is the compressed binary version of a Sequence Alignment Map (SAM). A SAM file consists of a Header section and an Alignment section. The Header section gives details about the file format and reference sequenced used in alignment, and the Alignment section gives information about each read that was aligned.
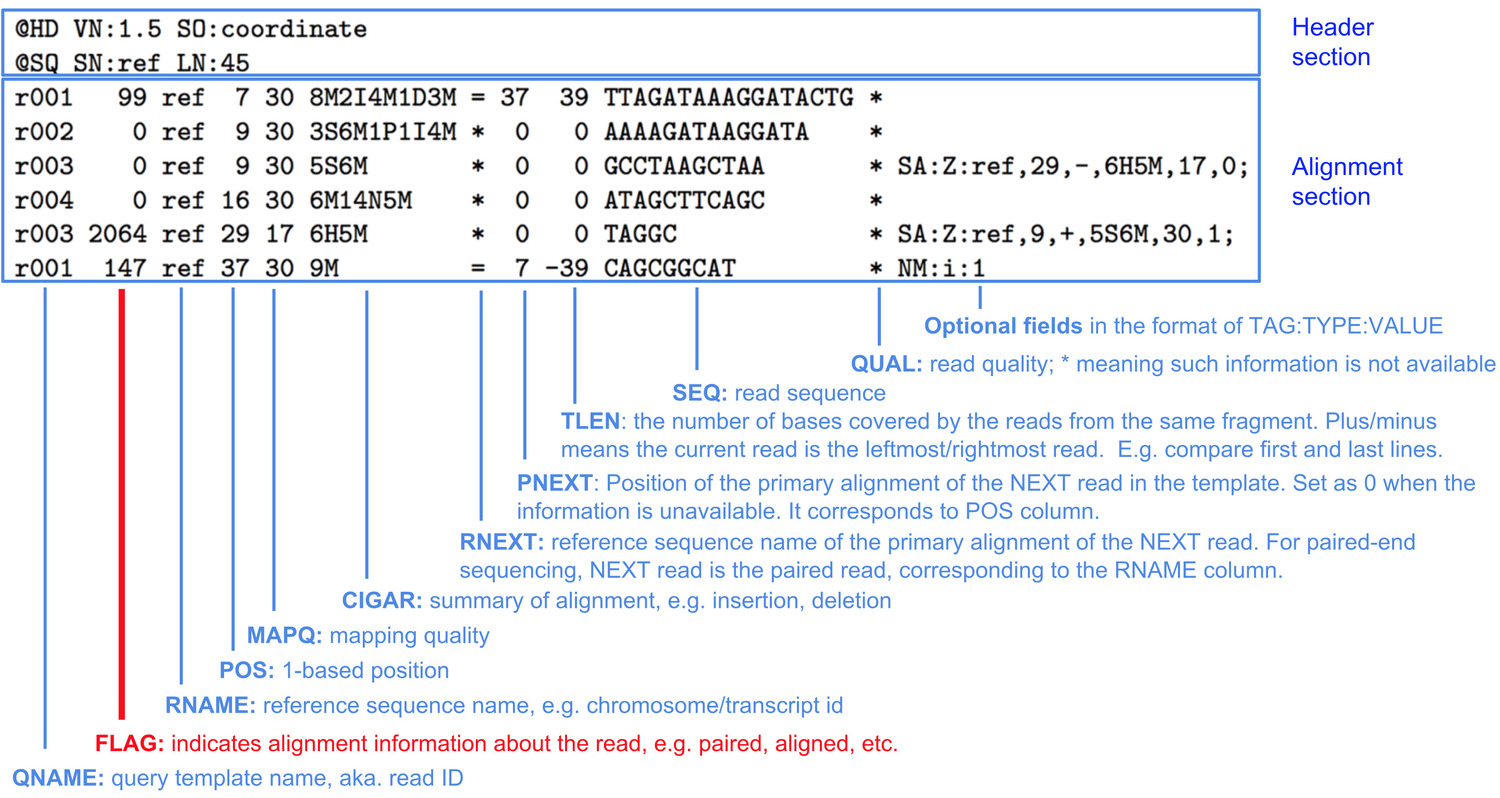
Image Source https://www.samformat.info/
(Optional) Run Samtools Flagstats to view aligment metrics
- In the Tools panel search bar, type flagstat and under the SAMTOOLS section, select Samtools flagstat
- Under BAM File to report statistics of select Map with BWA on collection 3.
- Click Execute
- Once the job is completed, you can view the results by clicking on the job, and clicking again on the
 icon in the completed SRR15607266 dataset.
icon in the completed SRR15607266 dataset. - The result is below and can be used to diagnose problems with the alignment quality
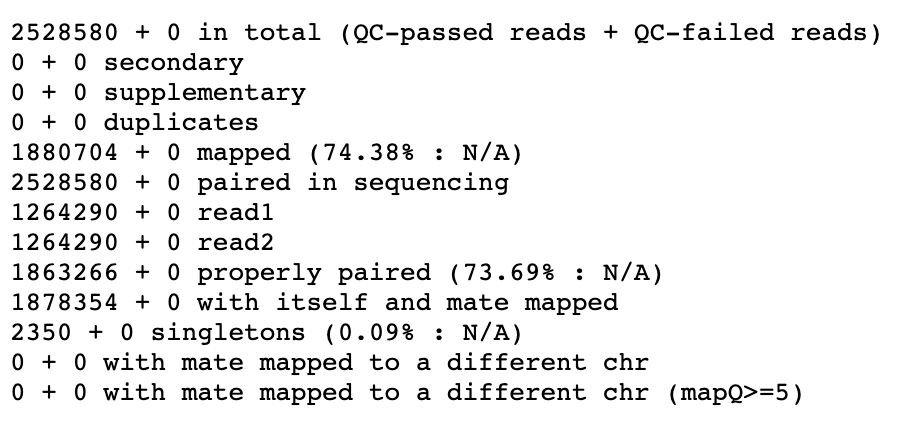
Result of Samtools Flagstat
Downsample BAM for quicker viewing
Before we view our alignment, we’ll downsample our BAM file to contain only a fraction of the original reads. This will be sufficient to view major variants present and confirm that we have sequenced the delta variant. NOTE: An alternative to this would be to increase the Maximum size of BAM chunks to 20,000,000 in the JBrowse settings in the following section, which will result in much slower loading of the sample.
- In the Tool panel search bar, type “downsample”
- Under Picard, select Downsample SAM/BAM
- In the Main panel, under Select SAM/BAM dataset or dataset collection click the folder icon
 and select Map with BWA on collection 3
and select Map with BWA on collection 3 - Under Probability (between 0 and 1) that any given read will be kept type 0.1 and press enter
- Click Execute
View Downsampled BAM file using JBrowse
JBrowse is a convenient tool that allows viewing of alignments, genomes and gene annotation within the Galaxy interface.
Configure JBrowse viewer
- In the Tools panel search bar, type JBrowse and select JBrowse genome browser
- Under Reference genome to display select Use a genome from history
-
Under Select the reference genome select genome (as fasta)
- Next we’ll add two Track groups, each with an annotation track
- Under Track Group click Insert Track Group
- Under Annotation Track click Insert Annotation Track
- First we’ll add the GFF track: Under Track Type select GFF/GFF3/BED Features and under GFF/GFF3/BED Track Data select genes.
- Next, well add the BAM track, so again click Insert Annotation Track
- Select track type BAM Pileups and under BAM Track Data click the folder icon
 and select the list Downsample SAM/BAM on collection 15: downsampled BAM
and select the list Downsample SAM/BAM on collection 15: downsampled BAM - Under Autogenerate SNP Track click Yes (SNP = Single Nucleotide Polymorphism. This will enable us to view changes in the sequence data with respect to the reference sequence)
- Scroll down and click Execute
- When the job is complete, it will show a new dataset in your history with the downsampled BAM.
Open JBrowse viewer
- Once the job is complete (green) click the
 icon on the JBrowse dataset.
icon on the JBrowse dataset. - In the Available Tracks panel select genes uncompressed
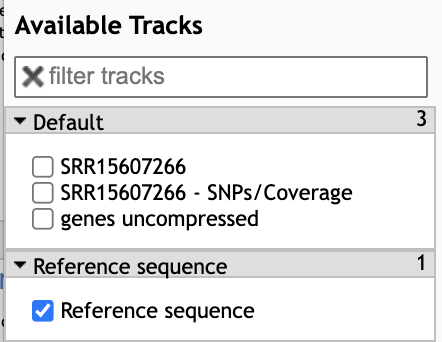
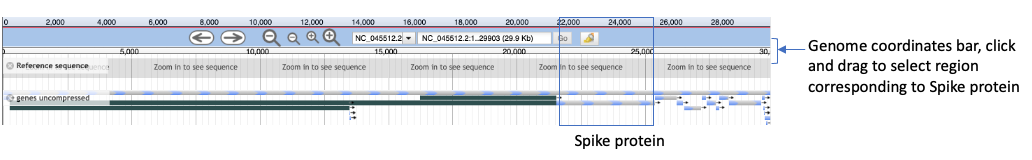
- In the center panel, you will see genome and gene features. We’ll click and drag on the Genome coordinates bar (indicated in the figure below) from approximately position 21,500-25,450 in order to zoom in on the Spike protein region (called surface glycoprotein).
- One can also type exact coordinates into the search bar (indicated in the figure below) to zoom in. Type in
22,995in the search bar and hit enter.
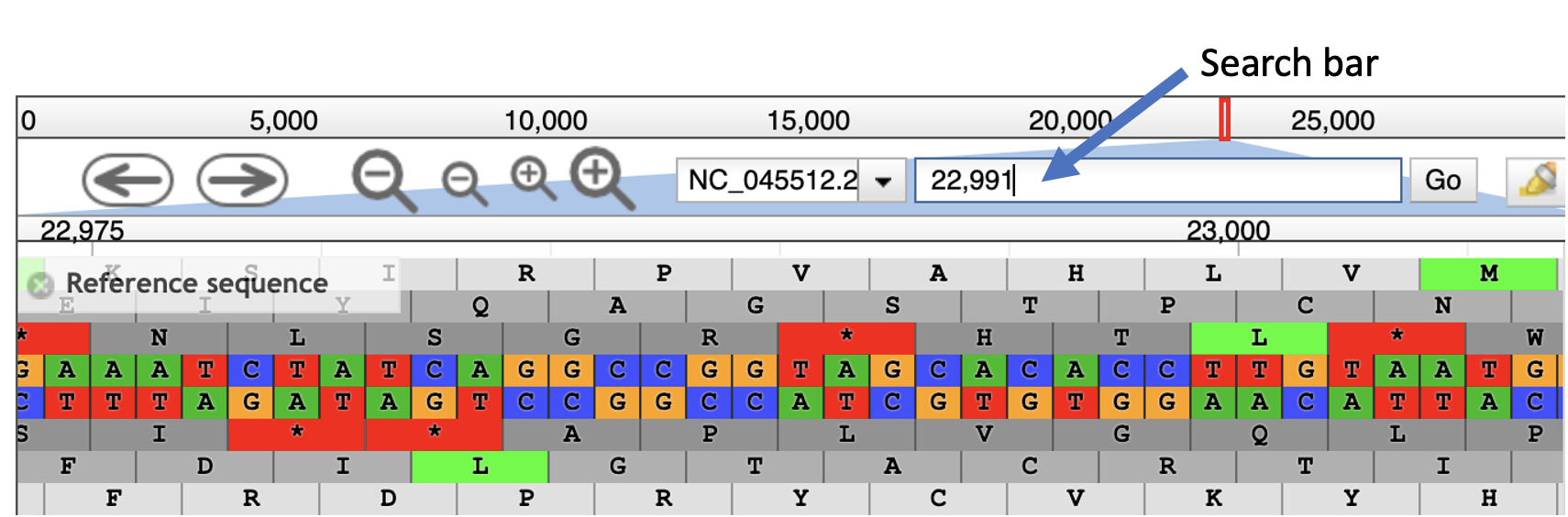
- Now we see a close-up of our reference sequence. The two center tracks show us the forward and reverse nucleotide sequence. Three reading frames for the reference sequence are shown in each direction.
- This region contains one of the 4 mutations that differentiate the delta variant from the originally characterized sequence. The amino acid change is a T>K change at protein position 478, which corresponds to a C>A SNP at nucleotide position 22,995. To see if this sample contains the mutation, select the two remaining tracks
- SRR15607266
- SRR15607266 - SNPs/Coverage
- We should see one variant represented both in the aligned reads as well as the coverage track.
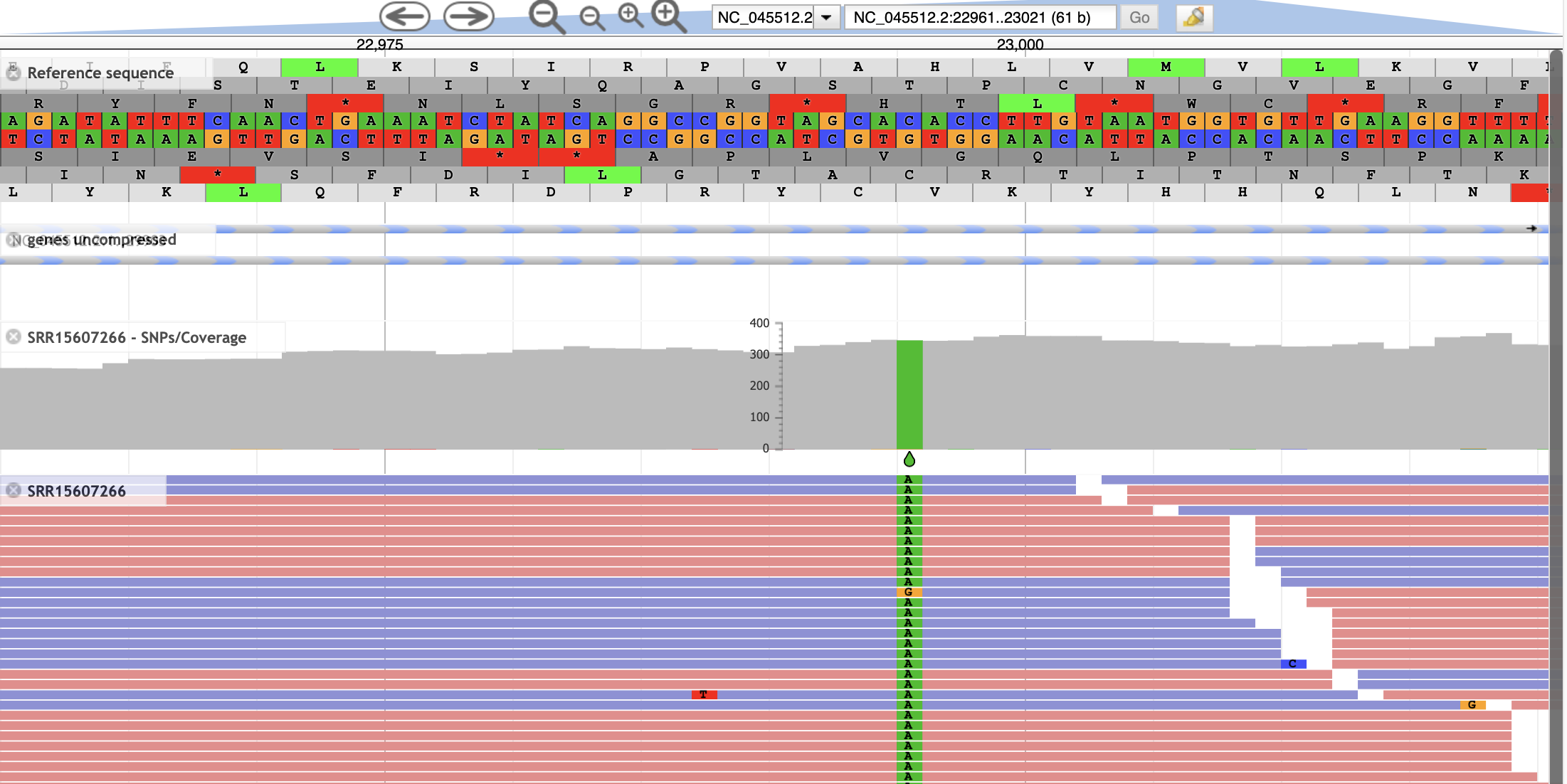
- The SRR15607266 - SNPs/Coverage track plots the number of reads aligned at each position, and additionally shows SNP that are present in >20% of the aligned reads.
-
The SRR15607266 shows each aligned read, coloring forward and reverse reads in blue and red, respectively, and indicating mismatches with the reference genome. Information about individual reads is available by clicking on the read.
- We can check another position to confirm that we have a delta variant sample:
- L452R: type
22,917in search bar
- L452R: type